ICSE Revision Notes for Preventive Measure of Pollution Class 9 Geography
Chapter Name | Preventive Measures for Pollution |
Topics Covered |
|
Related Study |
Abatement of Pollution
Air Pollution
At present, many cities are suffering from high levels of air pollution. The need of the hour is to make efforts to deal with it. Two methods are considered the most effective for dealing with the problem of air pollution. These are
Source Correction Methods: It is important to reduce air pollution from the source itself. In industries, this can be achieved by designing and developing schemes and processes which can minimise air pollution in the early stages.
In source correction methods, the following steps are taken:
- Change in Raw Materials: A raw material resulting in a large amount of air pollution should be replaced by eco-friendly raw materials.
• Liquefied petroleum gas or compressed natural gas should be used instead of coal and diesel to reduce air pollution.
• Fuel with low sulphur content should be used instead of fuel which has high sulphur content.
• Catalytic converters which go a long way in controlling the emission of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide should be used. - Change in Process: This includes the modification in the production process to reduce the contents of atmospheric pollution.
• The process of absorption is used to remove gaseous air pollutants. This is done by dissolving them in water or caustic soda. Absorption is used to remove sulphur dioxide, chlorine and nitrogen oxides.
• This process can also be used for removing pollutants from wastewater. The pollutants in water are made to attach with the surface of activated carbon. This carbon is then reacted with steam or carbon dioxide to produce activated carbon. This helps in the purification of water. - Modify the Existing Equipment: By modifying or altering equipment, the levels of pollution could be kept in check.
• Open hearth furnaces should be replaced with electrical or basic oxygen furnaces. This will reduce emission of smoke and carbon.
• Loss of hydrocarbons can be reduced from petroleum refineries by designing tanks with floating roof covers. - Maintenance of Equipment: It is important to maintain equipment which consumes more energy and produces more fumes. Leakages in tanks should also be looked after.
Pollution Control Equipment
Air pollution not only contains gaseous matter but also solid particles. Many devices and equipment have been designed to prevent air pollution. While choosing a device, any industry should keep the following points in mind:
- Amount of volume of particulate matter which has to be handled.
- Chemical and physical characteristics of the particulate along with its size.
- Temperature and humidity of gaseous medium.
- Concentration of gases in particulate size.
Pollution control devices are basically classified into two categories: devices which control particulate contamination and devices which control gaseous contamination.
Pollution Control Devices and their Functioning
Filters: Filters are used in electric power plants to separate particulate matter from gases. The device has a series of cloth bags through which the smoke passes. This helps in trapping the particulate matter in the bags.
Gravitational Settling Chamber
- A gravitational settling chamber is a rectangular chamber in which several horizontal trays are fixed.
- When the polluted gas stream enters the chamber, its velocity is kept low so that the particulates get sufficient time to settle because of gravity.
- The high-density pollutants settle at the bottom of the chamber and are then removed.
Scrubber
- A wet scrubber is a device which is used for trapping the emissions of water-soluble gases such as sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxide and ammonia.
- In a wet scrubber, spray nozzles are fitted through which water is sprayed into the device in a way that it goes downwards.
- As polluted gases rise upwards, their particulate matter collides with water drops. Because of the gravitational force, the water drops containing particulate matter settle at the bottom and the pollutants are segregated.
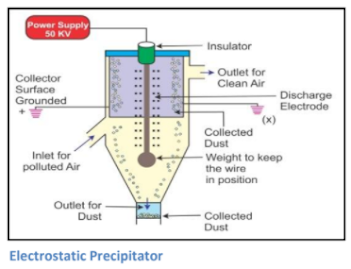
Electrostatic Precipitator
- This device is used for removing fly ash after combustion of coal or other materials. The process of its working is as follows:
- After combustion of coal and other materials, polluted gas or smoke enters the electrostatic precipitator.
- The device is electronically charged. The polluted air and impurities become negatively charged as they gain electrons on their surface.
- Negatively charged dust particles are then drawn towards the positively charged electrode plates and are deposited there.
- Impurities are then dislodged by mechanical rappers and get collected at the bottom of the unit in hopper.
- An electrostatic Precipitator is a very efficient device which removes more than 99% of impurities.
Cyclone Separator
It is a device which is used for removing impurities and particulate matter. It works in the following ways:
- Dust-laden air is made to enter the metallic cylinder at a high speed. It has a conical shape.
- As the speed of the air is high, a vortex or a whirlwind mass of the air is created.
- As a result the particulate matter falls to the bottom and the gas moves upwards.
- The particulate matter then slides down the walls of the cylinders and gets discharged from the outlet.
Water Pollution
Non-Point Sources
Sources of water pollution which cause inflow of pollutants over a large area are known as non-point sources. Example: Runoff from agricultural fields.
The following steps should be taken to reduce water pollution from non-point sources:
- Two separate drainages should be built for sewage and rainwater so that both rainwater and sewage do not overflow together.
- Nitrogen-fixing plants should be planted to reduce the use of chemical fertilisers.
- Agrochemicals and pesticides should be used judiciously to prevent them from draining into a water body.
- Efforts should be made to prevent runoff of manures.
- Biofertilisers and biopesticides should be used.
Point Sources
Sources which discharge pollutants to only one specific site are known as point sources. Example: Discharge of effluents from the factory into a river. To prevent pollution from point sources, it is essential to first treat wastewater before it is discharged. Laws should be made carrying strict punishment for discharging untreated wastewater into any water body.
Treatment of Plants
Wastewater should undergo three types of treatments to purify it. These are
- Primary treatment
- Secondary treatment
- Tertiary treatment
Primary Treatment
- In primary treatment of water, screens, grit chambers and sedimentation tanks are arranged in a serial order.
- Water which passes through them is treated with chlorine gas which kills the harmful bacteria in water. However, dissolved organic matter like salts cannot be treated in this method.
Secondary Treatment
- In this method, the organic matter which is present in water is biologically degraded by microorganisms. When water enters a tank, it comes into contact with microorganisms.
- Air is introduced into the tank through diffusers. Microorganisms in the presence of oxygen break the organic matter and the impurities then settle to the bottom of the tank which are later removed.
- Water is then treated with chlorine gas which then kills the rest of the harmful organisms.
Tertiary Treatment
In this method, nutrients such as nitrogen or phosphorus are removed. This water can be reused for industrial, agricultural and domestic purposes.
Methods to Control Soil Pollution
Land and soil pollution can be controlled by adopting the following measures:
Open Dumping
In open dumping, wastes are dumped in open spaces located far away from the limits of the city. This kind of waste disposal is not safe and has many limitations. The dumping of different types of wastes makes such dumping grounds as the breeding ground of mosquitoes and flies. Burning of these wastes also pollutes the air. The situation can become worse during rains. Rainwater may carry these wastes to nearby lakes, rivers or ponds and pollutes them.
Sanitary Landfills
Wastes are disposed away from the city in sanitary landfills. The waste is first spread in layers and then is compacted tightly so that their volume is reduced. The waste is then covered by soil and subjected to bacterial decomposition. Sanitary landfills are useful as the wastes are not attacked by rodents or insects. One precaution which needs to be taken is that landfills should not be located in areas which have high underground water level as it may get polluted.
Composting
In the composting method, household and municipal wastes are decomposed by the aerobic method. The wastes are decomposed by microorganisms.
This is a useful method of waste decomposition as wastes are decomposed by microorganisms into humus which add to the fertility of the soil.
Incineration
During incineration, municipal wastes are burned at a very high temperature. Many materials like metal do not get burnt. These are then recycled. This method however pollutes the air with fly ash and sulphur dioxide.
It is also an expensive process as proper devices for controlling air pollution need to be installed.
Segregation
This is a method in which wastes are segregated. Clothes, paper, glass and metals are stored in different bins.
Apart from these methods, effluents should be properly treated before they are discharged into the soil. Biofertilisers and manures should be used instead of chemical fertilisers.
Methods to Control Radioactive Pollution
The following steps should be taken to control nuclear pollution:
- Use of X rays should be minimised.
- Atomic or nuclear reactors should be regularly checked to ensure safety conditions.
- Nuclear devices should be tested deep underground.
- Production of radio isotopes should be minimised.
- In nuclear mines, wet drilling should be used along with underground drainage.
- Nuclear wastes should be handled with care and should be stored in shielded and corrosion-proof containers and then stored deep underground so that they may not escape and their proper decay takes place.
- Radiation levels should always be kept within the permissible limits.
- Radiation-resistant walls should be built around areas located close to nuclear reactors.
- Ground disposal of radiation wastes should be under approved rock and soil.