Frank Solutions for Chapter 3 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Class 9 Chemistry ICSE
1. Name:
(a) The most abundant element present in the Earth’s crust.
(b) The three most common elements present in the human body.
(c) Two elements that exist in the liquid state.
(d) One gaseous element which is
(i) Monoatomic
(ii) Diatomic
(e) Two metallic elements that can exists as liquids at about 30°C.
(f) Name two noble gases ?
Answer
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
(c) mercury, Bromine
(d) (i) Helium
(ii) Oxygen
(e) Gallium, caesium
(f) Two noble gases are-
(a) Helium
(b) Argon
2. Air is a mixture. Give points in support of this statement.
Answer
Air is a mixture because-
- The composition of air is not fixed i.e., the components may be present in any proportional by mass.
- Components of air i.e., nitrogen, oxygen etc. do not react with each other.
3. Classify the following into elements, mixtures and compounds: lead, gunpowder, air, petrol, ink, common salt, alcohol, sand, sodium and mercury.
Answer
Elements – Lead, Mercury, Sodium
Mixtures – Air, petrol, ink, gunpowder
Compounds – Common salt, alcohol and
4. What are pure and impure substances ? Give two examples of each.
Answer
- Pure substance: A pure substance is one which is made up of only one kind of particles. These particles may be atoms or molecules.
Example – Sulphur, Water. - Impure Substance: They are mixtures of two or more chemically different substances mixed in indefinite proportions. The constituent substances retain their properties in the mixture.
Example – Mixture of salt and sand, gunpowder
5. Name a metal and a non-metal which are liquids at room temperature.
Answer
Mercury is the metal which is liquid at room temperature and bromine is the non-metal which is liquid at room temperature.
6. What are the main differences compound and mixtures?
Answer
7. Draw a flow chart for the schematic representation of different types of matter.
Answer
The schematic representation of different types of matter is given below:
8. State two reasons for believing that copper is a metal and sulphur is a non-metal.
Answer
Two reasons for believing that copper is a metal and sulphur is a non-metal are: -
- Copper is malleable and ductile while sulphur is neither malleable nor ductile.
- Copper is a good conductor of heat while sulphur is not good conductor of heat.
9. What are the metalloids? Write two examples of metalloids.
Answer
Metalloids – The elements which possess properties intermediate between those of the metals and non-metals are called as metalloids. They react with both acids and alkali’s to form salts.
Example– arsenic, Antimony
10. Name a non-metal which is a good conductor of electricity.
Answer
Graphite is a non-metal which is a good conductor of electricity.
11. Compare the properties of metals and non-metals with respect to
(a) Malleability
(b) ductility
(c) conductivity
Answer
12. What is the general name of the materials which contain atleast two pure substances and show the properties of their constituents.
Answer
Mixture is the general name of the materials which contain atleast two pure substances and show the properties of their constituents.
13. Name the following:
(a) A metal stored in kerosene oil.
(b) A liquid non-metal.
(c) A metalloid.
(d) A radioactive noble gas.
(e) A liquid metal
(f) A solvent for rust
(g) A gas which is highly soluble in water.
Answer
(a) Sodium
(b) Bromine
(c) Arsenic
(d) Radon
(e) Mercury
(f) Oxalic acid
(g) Carbon dioxide
14. State the differences between an element and a compound.
Answer
15. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Elements cannot be broken into ……………….. by chemical or physical methods.
(b) An element is a pure substance in which the ……… number of each atom is same.
(c) Carbon is an element because the atomic number of each carbon atom is ………
(d) An example of a homogeneous mixture of a liquid and a solid is …………
(e) The atomicity of Oxygen is ……….
Answer
(a) Simpler substances
(b) atomic
(c) same
(d) mixture of salt and water
(e) two
16. Brass is a mixture of two elements namely copper and Zinc. Write the names of two other mixtures which contain elements only.
Answer
Names of two other mixtures which contain elements only are-
(a) Bronze
(b) Duralium
17. Define:
(a) A molecule
(b) Atomicity
Answer
(a) A molecule - The smallest particle of a substance that retains the chemical and physical properties of the substance and is composed of two or more atoms.
(b) Atomicity- Atomicity of an element is defined as the number of atoms present in one molecule of that element.
18. Why cannot a mixture be represented by a chemical formula?
Answer
Since, the constituents of a mixtures may be present in varying proportions so it cannot be expressed by a fixed chemical formula.
19. Name a mixture is used.
(a) By all living things.
(b) In the construction of buildings.
(c) As a food.
Answer
(a) Air
(b) Cement
(c) Milk Sugar Solution
20. What would you observe if a mixture of powdered iron and sulphur is heated in a test tube ?
Answer
If a mixture of powdered iron and sulphur is heated in a test tube, a black shiny compound iron (II) sulphide (FeS) is formed.
21. Name two elements which show exceptions to the properties of
(a) Metals
(b) Non-metals
Answer
(a) Tungsten, Mercury
(b) Graphite, Iodine
22. How many types of mixtures are known? Give examples also.
Answer
Based on their composition, there are two types of mixtures:
- Homogenous mixtures: These are the ones having a uniform composition throughout their bodies. Examples are a mixture of salt and water, sugar, and water, air, lemonade, soda water, etc.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: These are the ones that lack uniform composition throughout. Hence, a mixture of soil and sand, sulfur and iron filings, oil and water, etc.
23. Define the following terms and answer the association questions.
(a) Chromatography: State three advantages of Chromatography.
(b) Filtration: Give example of a mixture in which the components can be separated by this technique.
(c) Fractional distillation: Can a mixture of chloroform and water be separated by this method.
(d) Centrifugation: State one application of this method.
Answer
(a) Chromatography : The chromatography is a technique of separating pure substances from the mixture.
- It requires a very small amount of the substance or sample.
- Chromatography finds application in easy separation of substances with similar physical and chemical properties.
(b) Filtration – It is a separation technique for separating a mixture in which one component should be solid and insoluble in the other liquid component.
Example – Barium sulphate in water.
(c) Fractional distillation – It is a technique used to separate two liquids which dissolve in one another. The separation relies on the differences in boiling points of the two liquids.
No, mixture of chloroform and water cannot be separated by this method.
(d) Centrifugation: It is a method for separating the suspended particles of a substance from a liquid in which the mixture is rotated at a high speed in centrifuge machine..
Application – The clay particles in water (which are very fine) can be separated by centrifugation.
24. Explain the following terms:
(a) Sublimate
(b) Distillate
(c) Filtrate
(d) Supernatant liquid
(e) Sediment
Answer
(a) The vapour state which is obtained by heating solid without passing through liquid state is called sublimate.
(b) A liquid condensed from vapour in distillation is called distillate.
(c) The liquid produced after filtering a suspension of a solid in a liquid is called filtrate.
(d) Supernatant liquid is the upper layer of fluid found after a mixture has been centrifuged.
(e) If there is a heterogeneous mixture containing an insoluble solid in liquid, then the solid substance that settle down is called sediment.
25. What process would you use to separate alcohol (B.P. = 78° C) from a mixture of alcohol and water (B. P = 100 ° C)
Answer
We use fractional distillation to separate alcohol from a mixture of alcohol and water since the difference in boiling point between alcohol and mixture is very less.
26. Describe briefly how will you?
(a) Obtain pure water from sea water ?
(b) Obtain a sample of pure iodine and sodium chloride.
Answer
(a) We obtain pure water from sea water by distillation.
(b) A sample of pure iodine and sodium chloride is obtained by sublimation.
27. On what factors does the separation of the mixture depends?
Answer
The separation of the mixture depends upon-
(i) Size of the constituents
(ii) Magnetic properties of constituents
(iii) Mass of the constituents
(iv) Solubility of the constituents
(v) Miscibilities of the constituents
(vi) Boiling point of the constituents
(vii) Diffusion rate of the constituents
28. What is solvent extraction? Give an example of a separation of mixture by this method ?
Answer
This is a separation technique of solid-solid mixture. This method involves the use of a solvent in which only one of the solid present in the mixture dissolves. Unsolved solid is removed by filtration. Mixture of ammonium chloride and silver chloride is separated by this method.
29. (a) Name a technique to separate a mixture of two liquids?
(b) Can a mixture of Chloroform (B.P = 61°C) and carbon tetrachloride (B.P. = 77°C) be satisfactorily separated by the process you use for separating the various fractions of petroleum? What modifications will you make in the apparatus for this purpose?
Answer
(a) By distillation and fractional distillation we separate the mixture of two liquids.
(b) Yes, mixture of chloroform (B.P. = 61°C) and carbon tetrachloride (B.P. = 77°C) be satisfactorily separated by the process of fractional distillation which is used for separating the various fractions of petroleum.
For this purpose we will make two fractionating columns in the apparatus.
30. Name three different methods in each case for separation of
(a) Solid- solid mixtures
(b) Solid liquid mixtures
(c) Liquid-liquid mixtures
Give one example in each case.
Answer
(a) Solid-solid mixtures
- Magnetic separation method-Separation of iron ore from impurities
- Gravity separation – Mixture of saw dust and sand
- Solvent extraction-Mixture of sulphur and sand
(b) Solid-liquid mixtures
- Evaporation-Water and sodium chloride
- Distillation- Iodine in chloroform
- Filtration –Barium sulphate in water
(c) Liquid-liquid mixtures
- By separating funnel-oil and water mixture
- Distillation- Acetone and water
- Fractional distillation –Ethyl alcohol and water
31. What do you understand by chromatography? On what principal is it based?
Answer
The chromatography is the technique of separating pure substances from the mixtures. The chromatographic techniques was first employed by Russian scientist Michael Tswett in 1903 for the separation of coloured substance from the mixture.
Principle of chromatography: The principle of chromatography is based on the difference in the extent of interaction (absorption) of various substances with a stationary phase and a mobile phase. A substance which interacts strongly with the mobile phase goes ahead of the other substance which interacts strongly with the stationary phase.
32. How is chromatography applied in the separation of coloured constituents present in a mixture of ink ?
Answer
Ink generally contain more than one dye. This mixture of ink is used as moving phase. Different constituents of ink move at different speed. The solvent rises up the filter paper over the spot and carries the different coloured components of ink to different heights on the filter paper. Each spot thus obtained at a particular height on the filter paper contains a particular constituent of the ink. Thus, the component of the ink are separated.
33. Name the process used to separate the components of liquid air.
Answer
By the help of fractional distillation we separate the components of liquid air.
34. In which of the following four substances (sodium chloride, sodium carbonate crystals, sulphuric acid and iron) will there be
(a) increase in weight,
(b) decrease in weight,
(c) no change in weight
When exposed to air?
Answer
(a) Increase in weight – Sulphuric acid and iron
(b) Decrease in weight – Sodium carbonate crystals
(c) No change in weight – Sodium chloride
35. How will you separate a mixture of chalk powder and water?
Answer
By filtration, we will separate a mixture of chalk, powder and water.
36. Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the apparatus you would use to obtain pure water from a salt water mixture (or salt solution).
Answer
Pure water is obtained by distillation from a salt water mixture. The apparatus we would use to obtain pure water from a salt water mixture is given below –
37. What is the use of fractionating column in fractional distillation?
Answer
Fractionating column avoid the collection of distillate and re-distillation of distillate several times during fractional distillation.
38. Name two pair of liquids which can be separated by using a separating funnel.
Answer
Two pair of liquids which can be separated by using a separating funnel-
- Oil and water
- Chloroform and water
39. How will you separate camphor, common salt and iron nails from their mixture?
Answer
At first, with the help of magnet, iron nails will separate. Then, by sublimation camphor will separate from common salt.
40. Distinguish between the following terms with examples.
(a) decantation and filtration,
(b) filtrate and distillate
(c) fractional distillation and fractional crystallization,
(d) Metal and metalloid.
Answer
(a) Difference between decantation and filtration
(b) Difference between filtrate and distillate fractional distillation and fractional crystallization
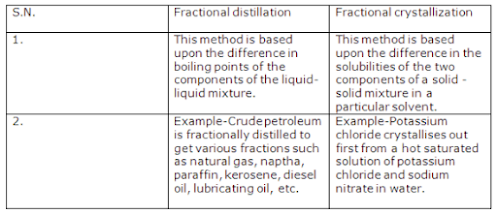
(c) Difference between fractional distillation and fractional crystallization
41. You are given two substances X and Y. X is a mixture of iron powder and sulphur. Y is powdered iron sulphide. What changes, if any will be observed in ‘X’ and ‘Y in each of the following cases:
(a) A magnet is moved over ‘X’ and ‘Y’ separately.
(b) ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are treated with carbon disulphide separately.
(c) ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are treated with dilute HCl separately. State the reason for the difference in the behavior of ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
Answer
(a) When a magnet is moved over ‘X’, iron fillings are pulled away and stick to the magnet. When a magnet is moved over’ Y’, it remained unaffected.
(b) When ‘X’ is treated with carbon disulphide, sulphur dissolves but not iron, While, when ‘Y’ is treated with carbon disulphide, iron sulphide does not dissolve but sinks to the bottom of the test tube.
(c) When ‘X’ is treated with dilute HCl, a colourless, odourless gas hydrogen is evolved which burns with a blue flame and is extinguished with a pop sound. While, when ‘Y’ is treated with dilute HCl, a colourless gas with the smell of rotten eggs is evolved which is H2S.
There is difference in the behaviour of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ because ‘X’ is a mixture while ‘Y’ is a compound. The component of a mixture do not react chemically, so retain their identity in the mixture while the components of compound react chemically, so do not retain their identity in the compound.
42. Name the process which is used in milk dairies to separate cream from milk.
Answer
Centrifugation is used in milk diaries to separate cream from milk dairies.