ICSE Solutions for Chapter 1 The Language of Chemistry Class 9 Selina Chemistry
Exercise 1A
1. What is a symbol? What information does it convey?
Solution
A symbol is the short form for the atom of a specific element or the abbreviations used to refer to the names of elements
(i) It represents a specific element.
(ii) It represents one atom of an element.
(iii) A symbol represents how many atoms are present in its one gram (gm) atom.
(iv) It represents the number of times an atom is heavier than one atomic mass unit (amu) taken as a standard.
2. Why is the symbol S for Sulphur, but Na for Sodium and Si for Silicon?
Solution
For most of the element, the first letter of the name of the element is taken as the symbol for that element and written in capitals (e.g. for Sulphur, we use the symbol S). In cases where the first letter has already been used for naming another element, we use a symbol derived from the Latin name of that element (e.g. for sodium/Atrium, we use the symbol Na). In some cases, we use the initial letter in capital together with a small letter from its name (e.g. for silicon, we use the symbol Si).
3. Write the full form of IUPAC. Name the elements represented by the following Symbols: Au, Pb, Sn, Hg
Solution
IUPAC stands for The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
Au- Gold
Pb- Lead
Sn- Tin
Hg- Mercury
4. If the symbol for cobalt, Co were written as CO, What would be wrong with it?
Solution
Co represents Cobalt. If we write CO then it means it consists of two different non-metals namely Carbon and Oxygen which will represent Carbon-monoxide but not Cobalt.
C represents Carbon and O represents Oxygen.
5. What do the following symbols stand for?
(a) H
(b) H2
(c) 2H
(d) 2H2
Solution
(a) One Hydrogen atom
(b) Hydrogen molecules
(c) Two Atom of hydrogen
(d) Two molecules of hydrogen.
6. What is meant by atomicity? Name the diatomic element.
Solution
The number of atoms of an element which join together to form a molecule is known as atomicity of that element.
Diatomic molecules: H2, O2, N2, Cl2
7. (a) Explain the terms ‘valence’ and ‘variable valency.
(b) How are the elements with variable valence named? Explain with an example.
Solution
(a) Valence of Na is +1 because it can lose one electron.
Valence of O is -2 because it can accept two electrons.
Variable valence: It is the combining capacity of an element in which the metal loses more electrons from a shell next to a valence shell in addition to electrons of the valence shell.
(b) If an element exhibits two different positive valences, then
for the lower valence, use the suffix -OUS at the end of the name of the metal
for the higher valency, use the suffix -IC at the end of the name of the metal.
Example:
|
Element |
Lower valence |
Higher valency |
|
Ferrum (Iron) |
Ferrous (Fe2+) |
Ferric (Fe3+) |
8. Give the formula and valency of
(a) aluminate(b) chromate
(c) aluminium
(d) cupric
Solution
|
Name |
Formula |
Valency |
|
Aluminate |
AlO2 |
-2 |
|
Chromate |
CrO4 |
-2 |
|
Aluminium |
Al |
+3 |
|
Cupric |
Cu |
+2 |
9. (a) What is a chemical formula?
(b) What is the significance of a formula? Give an example to illustrate.
Solution
(a) A chemical formula is a symbolic representation of the number of atoms present in a molecule of that substance.(b) Significance of the molecular formula:
- It represents both molecule and molecular mass of the compound.
- It represents the respective number of different atoms present in one molecule of the compound.
- It represents the ratios of the respective masses of the elements present in the compound.
Example: Salt: NaCl, Ethanol C2H6O because the molecule of ethanol contains two Carbon, 6 Hydrogen and 1 Oxygen atom.
10. What do you understand by the following terms?
(a) Acid radical
(b) Basic radical
Solution
(a) Acid radical: The electronegative or negatively charged radical is called an acid radical.
Examples: Cl–, O2-
(b) Basic radical:The electropositive or positively charged radical is called a basic radical.
Examples: K+, Na+
11. Select the basic and acidic radicals in the following compounds.
(a) MgSO4
(b) (NH4)2SO4
(c) Al2 (SO4)3
(d) ZnCO3
(e) Mg (OH) 2
Solution
Acidic radical | Basic radical | |
a. MgSO4 | SO4– | Mg+ |
b. (NH4)2SO4 | SO4– | NH4+ |
c. Al2(SO4)3 | SO4– | Al3+ |
d. ZnCO3 | CO3– | Zn2+ |
e. Mg(OH)2 | OH– | Mg2+ |
12. Write chemical formula of the sulphate of Aluminum, Ammonium and Zinc.
Solution
Valences of aluminum, ammonium and zinc are 3, 1 and 2, respectively. The valences of sulphate is 2.
Hence, chemical formulae of the sulphates of aluminum, ammonium and zinc are Al2(SO4)3, (NH4)2SO4 and ZnSO4.
13. The valence of an element A is 3 and that of element B is 2. Write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of A and B.
Solution
Formula of the compound = A2B3
14. Match the following:
|
Compound |
Formula |
|
Boric acid |
NaOH |
|
Phosphoric acid |
SiO2 |
|
Nitrous acid |
Na2CO3 |
|
Nitric acid |
KOH |
|
Sulphurous acid |
CaCO3 |
|
Sulphuric acid |
NaHCO3 |
|
Hydrochloric acid |
H2S |
|
Silica (Sand) |
H2O |
|
Caustic soda ( Sodium Hydroxide) |
PH3 |
|
Caustic potash( potassium hydroxide) |
CH4 |
|
Washing soda( Sodium carbonate) |
NH3 |
|
Baking Soda ( Sodium bicarbonate) |
HCl |
|
Limestone ( calcium carbonate) |
H2SO3 |
|
Water |
HNO3 |
|
Hydrogen Sulphide |
HNO2 |
|
Ammonia |
H3BO3 |
|
Phosphine |
H3PO4 |
|
Methane |
H2SO4 |
Solution
|
Compound |
Formula |
|
Boric acid |
H3BO3 |
|
Phosphoric acid |
H3PO4 |
|
Nitrous acid |
HNO2 |
|
Nitric acid |
HNO3 |
|
Sulphurous acid |
H2SO3 |
|
Sulphuric acid |
H2SO4 |
|
Hydrochloric acid |
HCl |
|
Silica (Sand) |
SiO2 |
|
Caustic soda ( Sodium Hydroxide) |
NaOH |
|
Caustic potash( potassium hydroxide) |
KOH |
|
Washing soda( Sodium carbonate) |
Na2CO3 |
|
Baking Soda ( Sodium bicarbonate) |
NaHCO3 |
|
Limestone ( calcium carbonate) |
CaCO3 |
|
Water |
H2O |
|
Hydrogen Sulphide |
H2S |
|
Ammonia |
NH3 |
|
Phosphine |
PH3 |
|
Methane |
CH4 |
15. Write the basic radicals and acidic radicals of the following and then write the chemical formulae of these compounds.
(a) Barium sulphate
(b) Bismuth nitrate
(c) Calcium bromide
(d) Ferrous sulphide
(e) Chromium sulphate
(f) Calcium silicate
(g) Stannic oxide
(h) Sodium zincate
(i) Magnesium phosphate
(j) Sodium thiosulphate
(k) Stannic phosphate
(l) Nickel bisulphate
(m) Potassium manganite
(n) Potassium Ferro cyanide
Solution
|
Compounds |
Acidic radical |
Basic radical |
Chemical formulae |
|
Barium sulphate |
SO42- |
Ba2+ |
BaSO4 |
|
Bismuth nitrate |
NO3– |
Bi3+ |
Bi(NO3)3 |
|
Calcium bromide |
Br– |
Ca2+ |
CaBr2 |
|
Ferrous sulphide |
S2- |
Fe2+ |
FeS |
|
Chromium sulphate |
SO42- |
Cr3+ |
Cr2(SO4)3 |
|
Calcium silicate |
SiO42- |
Ca2+ |
Ca2SiO4 |
|
Potassium ferrocyanide |
[Fe(CN)6]4- |
K1+ |
K4[Fe(CN)6] |
|
Stannic oxide |
O2- |
Sn2+ |
SnO2 |
|
Magnesium phosphate |
(PO4)3- |
Mg2+ |
Mg3(PO4)2 |
|
Sodium zincate |
ZnO2- |
Na1+ |
Na2ZnO2 |
|
Stannic phosphate |
(PO4)3- |
Sn4+ |
Sn3(PO4)4 |
|
Sodium thiosulphate |
(S2O3)2- |
Na1+ |
Na2S2O3 |
|
Potassium manganate |
MnO42- |
K1+ |
K2MnO4 |
|
Nickel bisulphate |
HSO41- |
Ni3+ |
Ni(HSO4)3 |
16. Write the chemical names of the following compounds:
(a) Ca3 (PO4)2
(b) K2CO3
(c)K2MnO4
(d) Mn3 (BO3)2
(e) Mg (HCO3)2
(f) Na4Fe (CN)6
(g) Ba (ClO3)2
(h) Ag2SO3
(i) (CH3COO)2Pb
(j) Na2SiO3
Solution
Chemical names of compounds:
Ca3(PO4)2– Calcium phosphate
K2CO3– Potassium carbonate
K2MnO4 – Potassium manganite
Mn3(BO3)2– Manganese (II) borate
Mg(HCO3)2– Magnesium hydrogen carbonate
Na4Fe(CN)6– Sodium Ferro cyanide
Ba(ClO3)2– Barium chlorate
Ag2SO3– Silver sulphite
(CH3COO)2Pb – Lead acetate
Na2SiO3– Sodium silicate
17. Give the names of the following compounds.
(a) KClO
(b) KClO2
(c) KClO3
(d) KClO4
Solution
(a) Potassium hypochlorite
(b) Potassium chlorate
(c) Sodium chlorate
(d) Sodium perchlorate
18. Complete the following statements by selecting the correct option.
(a) The formula of a compound represents- an atom
- a particle
- a molecule
- a combination
- AlO3
- AlO2
- Al2O3
- Al3O2
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Solution
(a) iii. The formula of a compound represents a molecule.
(b) iii. The correct formula of aluminum oxide is Al2O3.
(c) iv. The valence of nitrogen in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is four.
19. Give the names of the elements and number of atoms of those elements present in the following compounds.
- Sodium sulphate
- Quick lime
- Baking soda (NaHCO3)
- Ammonia
- Ammonium dichromate
Solution
- Sodium sulphate – Na2SO4
There are two sodium atoms, one Sulphur atom and four oxygen atoms.
- Quick lime – CaO
There is one calcium atom and one oxygen atom.
- Baking soda – NaHCO3
There is one sodium, carbon and hydrogen atom and three oxygen atoms.
- Ammonia – NH3
There is one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms.
- Ammonium dichromate – (NH4) Cr2O7
There two ammonium atoms, two chromium atoms and seven oxygen atoms.
20. The formula of the sulphate of an element M is M2(SO4)3. Write the formula of its:
- Chloride
- Oxide
- Phosphate
- Acetate
Solution
The valence of metal M is 3. So, the formulae are as follows:
- Chloride – MCl3
- Oxide – M2O3
- Phosphate – M(PO4)
- Acetate – M(CH3COO)3
Exercise 1B
1. What is a chemical equation? Why it is necessary to balance it?
Solution
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using the symbols and formulae of the substances which are involved in the reaction.
Necessity for balancing a chemical equation:
A chemical equation needs to be balanced because a chemical reaction is just a rearrangement of atoms.
Atoms themselves are neither created nor destroyed during the course of a chemical reaction.
The chemical equation needs to be balanced to follow the law of conservation of mass.
2. State the information conveyed by the following equation:
Zn(s) + 2HCl (aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2↑
Solution
A solid metal zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid in the aqueous state to produce zinc chloride in the aqueous state and hydrogen gas.
3. What is the limitation of the reaction given in question 2?
Solution
The chemical equation given in question 2 does not give the time taken for the completion of the reaction.
Also, it does not give information about whether heat is absorbed or evolved during the reaction.
4. Write the chemical equations for the following word equations and balance them.
(a)Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide
(b)Nitrogen + Oxygen → Nitrogen monoxide
(c) Calcium + Nitrogen → Calcium nitride
(d)Calcium oxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate
(e)Magnesium+ Sulphuric acid → Magnesium sulphate + Hydrogen
(f) Sodium reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen
Solution
(a) C + O2→ CO2
(b) N2 + O2→ 2NO
(c) 3Ca + N2→ Ca3N2
(d) CaO + CO2→ CaCO3
(e) Mg + H2SO4→ MgSO4 + H2↑
(f) Na + H2O → NaOH + H2↑
5. Balance the following equations:
(a) Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
(b) Ca + N2 → Ca3N2
(c) Zn + KOH → K2ZnO2 + H2
(d) Fe2O3 + CO → Fe + CO2
(e) PbO + NH3 → Pb + H2O + N2
(f) Pb3O4 → PbO + O2
(g) PbS + O2 → PbO + SO2
(h) S + H2SO4 → SO2 + H2O
(i) S + HNO3 → H2SO4 + NO2 + H2O
(j) MnO2 + HCl → MnCl2 + H2O + Cl2
(k) C + H2SO4 → CO2 + H2O + SO2
(l) KOH + Cl2 → KCl + KClO + H2O
(m) NO2 +H2O → HNO2 + HNO3
(n) Pb3O4 + HCl → PbCl2 + H2O + Cl2
(o) H2O + Cl2 → HCl + O2
(p) NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
(q) HNO3 + H2S → NO2 + H2O + S
(r) P + HNO3 → NO2 + H2O + H3PO4
(s) Zn + HNO3 → Zn (NO3)2 + H2O + NO2
Solution
Balanced chemical equations:
(a) 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
(b) 3Ca + N2 → Ca3N2
(c) Zn + 2KOH → K2ZnO2 + H2
(d)Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
(e) 3PbO + 2NH3 → 3Pb + 3H2O + N2
(f) 2Pb3O4 → 6PbO + O2
(g) 2PbS + 3O2 → 2PbO + 2SO2
(h)S + 2H2SO4 → 3SO2 + 2H2O
(i)S + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + 6NO2 + 2H2O
(j) MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
(k) C + 2H2SO4 → CO2 + H2O + SO2
(l) 2KOH + Cl2 → KCl + KClO + H2O
(m) 2NO2 + H2O → HNO2 + HNO3
(n) Pb3O4 + 8HCl → 3PbCl2 + 4H2O + Cl2
(O) 2H2O + 2Cl2 → 4HCl + O2
(p) 2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
(q) 2HNO3 + H2S → 2NO2 + 2H2O + S
(r) P + 5HNO3 → 5NO2 + H2O + H3PO4
(s) Zn + 4HNO3 → Zn (NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
Exercise 1C
1 Fill in the blanks:
(a) Dalton used symbol _____ for oxygen _____ for hydrogen.
(b) Symbol represents _____ atom(s) of an element.
(c) Symbolic expression for a molecule is called _____. .
(d) Sodium chloride has two radicals. Sodium is a _____ radical while chloride is _____ radical.
(e) Valence of carbon in CH4 is _____, in C2H6 _____, in C2H4 ___ and in C2H2 is ____.
(f) Valence of Iron in FeCl2 is _____ and in FeCl3 it is ____.
(g) Formula of iron (ill) carbonate is _____.
Solution
(a) Dalton used symbol ‘O’ for oxygen, ‘H’ for hydrogen.
(b) Symbol represents gram atom(s) of an element.
(c) Symbolic expression for a molecule is called molecular formula.
(d) Sodium chloride has two radicals. Sodium is a basic radical, while chloride is an acid radical.
(e) Valence of carbon in CH4 is 4, in C2H6 4, in C2H4 4 and in C2H2 is 4.
(f) Valence of iron in FeCl2 is 2 and in FeCl3 it is 3.
(g) Formula of iron (III) carbonate is Fe2 (CO3)3.
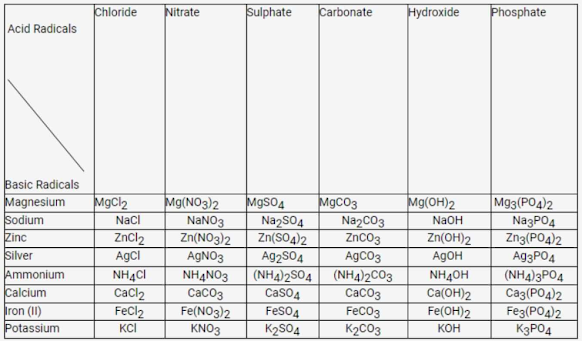
2. Complete the following table.
3. Sodium chloride reacts with silver nitrate to produce silver chloride and sodium nitrate
(a) Write the equation.
(b)Check whether it is balanced, if not balance it.
(c)Find the weights of reactants and products.
(d) State the law which this equation satisfies.
Solution
(a) NaCl + AgNO3→ NaNO3 + AgCl↓
(b) It is a balanced equation.
(c) Weights of reactants: NaCl - 58.44, AgNO3 – 169.87
Weights of products: NaNO3 – 84.99, AgCl – 143.32
(d) Law of conservation of mass: Matter is neither created nor destroyed in the course of a chemical reaction.
4. What information does the following chemical equation convey?
(a) Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4+ H2
(b) Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2+ H2
Solution
(a) The actual result of a chemical change.
Substances take part in a reaction, and substances are formed as a result of the reaction.
- Here, one molecule of zinc and one molecule of sulphuric acid react to give one molecule of zinc sulphate and one molecule of hydrogen.
- Composition of respective molecules, i.e. one molecule of sulphuric acid contains two atoms of hydrogen, one atom of sulphur and four atoms of oxygen.
- Relative molecular masses of different substances, i.e. molecular mass of
Zn = 65
H2SO4 = (2+32+64) = 98
ZnSO4 = (65+32+64) = 161
H2 = 2
- 22.4 liters of hydrogen are formed at STP.
(b) This equation conveys the following information:
- Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas.
- 24 g of magnesium reacts with 2(1 + 35.5) = 73 g of hydrochloric acid to produce (24 + 71), i.e. 95 g of magnesium chloride.
- Hydrogen produced at STP is 22.4 liters.
5. (a)What are polyatomic ions? Give two examples.
(b) Name the fundamental law that is involved in. every equation
Solution
(a) A polyatomic ion is a charged ion composed of two or more covalently bounded atoms.
(b) Fundamental laws which are involved in every equation:
- A chemical equation consists of formulae of reactants connected by a plus sign (+) and arrow (→) followed by the formulae of products connected by the plus sign (+).
- The sign of an arrow (→) is to read ‘to form’. It also shows the direction in which the reaction is predominant.
- The fundamental law followed by every equation is ‘Law of Conservation of Mass’.
6. What is the valence of?
(a)Fluorine in CaF2
(b) Sulphur in SF6
(c) Phosphorus in PH3
(d) Carbon in C4
(e) Nitrogen in the following compounds:
(i) N2O5
(ii) N2O3
(iii) NO2
(iv) NO
(f) Manganese in MnO2
(g) Copper is Cu2O
(h) Magnesium in Mg3
Solution
(a) Fluorine in CaF2 is -1.
(b) Sulphur in SF6 is -6.
(c) Phosphorus in PH3 is +3.
(d) Carbon in CH4 is +4.
(e) Valence of nitrogen in the given compounds:
(i) N2O3 = N is +3
(ii) N2O5 = N is +5
(iii) NO2 = N is +4
(iv) NO = N is +2
7. Why should an equation be balanced? Explain with the help of a simple equation.
Solution
According to the law of conservation of mass, ‘matter can neither be created nor can it be destroyed’. This is possible only if the total number of atoms on the reactants side is equal to the total number of atoms on the products side. Thus, a chemical reaction should always be balanced.
Example: KNO3 → KNO2 + O2
In this equation, the number of atoms on both sides is not the same, and the equation is not balanced. The balanced form of this equation is:
2KNO3 → 2KNO2 + O2
8. Write the balanced chemical equations of the following word equation.
(a) Sodium hydroxide + sulphuric acid → sodium sulphate + water
(b) potassium bicarbonate + sulphuric acid → potassium sulphate + carbon dioxide + water
(c) iron + sulphuric acid → ferrous sulphate + hydrogen.
(d) chlorine + sulphur dioxide + water → sulphuric acid + hydrogen chloride
(e) silver nitrate → silver + nitrogen dioxide + oxygen
(f) copper + nitric acid → copper nitrate + nitric oxide + water
(g) ammonia + oxygen → nitric oxide + water
(h) barium chloride + sulphuric acid → barium sulphate + hydrochloric acid
(i) zinc sulphide + oxygen → zinc oxide + sulphur dioxide
(j) aluminium carbide + water → aluminium hydroxide + methane
(k) iron pyrites(FeS2) + oxygen → ferric oxide + sulphur dioxide
(l) potassium permanganate + hydrochloric acid → potassium chloride + manganese chloride + chlorine + water
(m) aluminium sulphate + sodium hydroxide → sodium sulphate + sodium meta aluminate + water.
(n) aluminium + sodium hydroxide + water → sodium meta aluminate + hydrogen
(o) potassium dichromate + sulphuric acid → potassium sulphate + chromium sulphate + water + oxygen.
(p) potassium dichromate + hydrochloric acid → Potassium chloride + chromium chloride + water + chlorine
(q)sulphur + nitric acid → sulphuric acid + nitrogen dioxide + water.
(r) sodium chloride + manganese dioxide + sulphuric acid → sodium hydrogen sulphate + manganese sulphate + water + chlorine.
Solution
(a) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(b) 2KHCO3 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2CO2 + 2H2O
(c)Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2
(d) Cl2 + SO2 + 2H2O → H2SO4 + 2HCl
(e) 2AgNO3 → 2Ag + 2NO2 + O2
(f) 3Cu + 8HNO3 → 3Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO + 4H2O
(h) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
(i) 2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2
(j) Al4C3 + 12H2O → 4Al(OH)3 + 3CH4
(k) 4FeS2 + 11O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2
(l) 2KMnO4 + HCl → 2KCl + 2MnCl2 + 5Cl2 + 8H2O
(m) Al2(SO4)3 + 8NaOH → 3Na2SO4 + 2NaAlO2 + 4H2O
(n) 2Al + 2NaOH + 2H2O → 2NaAlO2 + 3H2
(o) 2K2Cr2O7 + 8H2SO4 → 2K2SO4 + 2Cr2(SO4)3 + 8H2O + 3O2
(p) K2Cr2O7 + 14HCl → 2KCl + 2CrCl3 + 7H2O + 3Cl2.
(q) S + HNO3 → H2SO4 + NO2 + H2O
(r) 2NaCl + MnO2 + 3H2SO4 → 2NaHSO4 + MnSO4 + 2H2O + Cl2
9. (a)Define atomic mass unit.
(b) Calculate the molecular mass of the following:
(I) Na2SO4.10H2O
(ii) (NH4)2CO3
(iii) (NH2)2CO
(iv) Mg3N2
Given atomic mass of Na = 23, H = 1, O = 16, C = 12, N = 14, Mg = 24, S = 32.
Solution
(a) Atomic mass unit (amu) is equal to one-twelfth the mass of an atom of carbon-12 (atomic mass of carbon taken as 12).
(b) (i) The relative molecular mass of CuSO4.5H2O
= 63.5 + 32 + (16×4) + 5(2+16)
= 159.5 + 90
= 249.5
(ii) The relative molecular mass of (NH4)2CO3 = N2H8CO3= (14×2) + (1×8) + 12 + (3×16)
= 28 + 8 + 12 + 48
(iii) The relative molecular mass of (NH2)2CO = N2H4CO= (2×14) + (1×4) + 12 + 16
= 28 + 4 + 12 + 16 = 60
(iv) The relative molecular mass of Mg3N2= (3×24) + (2×14)
= 72 + 28
= 100
10. Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) Modern atomic symbols are based on the method proposed by
(i) Bohr
(ii) Dalton
(iii) Berzelius
(iv) Alchemist
(b) The number of carbon atoms in a hydrogen carbonate radical is
(i) One
(ii) Two
(iii) Three
(iv) Four
(c) The formula of iron (III) sulphate is
(i) Fe3SO4
(ii) Fe (SO4)3
(iii) Fe2 (SO4)3
(iv) FeSO4
(d) In water, the hydrogen-to-oxygen mass ratio is
(ii) 1: 8
(ii) 1: 16
(iii) 1: 32
(iv) 1: 64
(e) The formula of sodium carbonate is Na2CO3 and that of calcium hydrogen carbonate is
(i) CaHCO3
(ii) Ca (HCO3)2
(iii) Ca2HCO3
(iv) Ca (HCO3)3
Solution
(a) iii. Berzelius
(b) i. One
(c) iii. Fe2(SO4)3
(d) i. 1:8
(e) ii. Ca(HCO3)2
11. Correct the following Statement
(a)A molecular formula represent an elements.
(b) Molecular formula of water is H2O2.
(c) A molecule of Sulphur is monoatomic.
(d) CO and Co both represent cobalt.
(e) Formula of iron (III) oxide is FeO.
Solution
(a) Molecular formula represents molecule of an element or a compound.
(b) Molecular formula of water is H2O.
(c) A molecule of Sulphur is diatomic.
(d) Formula of iron(III)oxide is Fe2O3.
12. Calculate the relative molecular masses of:
(a) CHCl3
(b) (NH4)2Cr2O7
(c) CuSO4.5H2O
(d) (NH4)2SO4
(e) CH3COONa
(f) potassium chlorate
(g) Ammonium chloroplatinate = (NH4)2 SO4
[At. Mass: C = 12, H =1, O = 16, Cl = 35.5, N = 14, Cu = 63.5, S =32, Na = 23, K = 39, Pt = 195, Ca = 40, P =31 Mg = 24,]
Solution
(a) Relative molecular mass of CHCl3
= 12 + 1 + (3×35.5)
= 12 + 1 + 106.5
= 119.5
(b) Relative molecular mass of (NH4)2 Cr2O7
= (14×2) + (1×8) + (52×2) + (16×7)
=28 + 8 + 104 + 112
=252
(c) Relative molecular mass of CuSO4.5H2O
=63.5 + 32 + (16×4) + 5(2 + 16)
= 159.5 + 90
= 249.5
(d) Relative molecular mass of (NH4)2SO4
= (2×14) + (8×1) + 32 + (4×16)
=28 + 8 + 32 + 64
= 132
(e) Relative molecular mass of CH3COONa
= (12×2) + (1×3) + (16×2) + 23
= 24 + 3 + 32 + 23
= 82
(f) Potassium chlorate (KClO3)
= 39.1 + 35.5 + (16×3)
= 39.1 + 35.5 + 4
= 122.6
(g) Ammonium chloroplatinate (NH4)2PtCl6
= (14×2) + (1×8) + 195.08 + (35.5×6)
= 28+ 8 +195.08 + 213
= 444.08
13. Give the empirical formula of:
(a) Benzene(C6H6)
(b) Glucose(C6H12O6)
(c) Acetylene(C2H2)
(d) Acetic acid(CH3COOH)
Solution
(a) Benzene-CH
(b) Glucose- CH2O
(c) Acetylene- CH
(d) Acetic acid-CH2O
14. Find the percentage mass of water in Epsom salt MgSO4.7H2O.
Solution
Relative molecular mass of MgSO4.7H2O
= 24 + 32 + (16×4) + 7(2 + 16)
= 24 + 32 + 64 + 126
= 246
26 g of Epsom salt contains 126 g of water of crystallisation. Hence, 100 g of Epsom salt contains 100×126/246.
The % of H2O in MgSO4.7H2O = 51.2
(a) Calcium hydrogen phosphate Ca(H2PO4)2
(b) Calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2
Solution
(a) Relative molecular mass of Ca(H2PO4)2
= 40.07 + (1×4) + (30.9×2) + (16×8)
= 40.07 + 4 + 61.8 + 128
= 233.87
233.87 g Ca(H2PO4), contains 61.8 g P.
So, 100 g Ca(H2PO4)2 contains
The % of Pin Ca(H2PO4)2 is 26.42%
(b) Relative molecular mass of Ca3(PO4)2
= (40.07 ×3) + (30.9×2) + (16 ×8)
= 120.21 + 61.8 + 128
= 310.01
310.01 g Ca3(PO4)2 contains 61.8 g P.
So, 100 g Ca(H2PO4)2 contains
The % of P in Ca3(PO4)2 is 19.93%.
16. Calculate the percentage composition of each clement in Potassium chlorate, KCIO.
Solution
Relative molecular mass of KClO3
= 39.09 + 35.5 + (3×16)
= 122.59 g
122.59 g KClO3 contains 39.09g K
Hence, 100 g KClO3 contains
122.59 g KClO3 contains 35.5 g Cl
Hence, 100 g KClO3 contains
122.59 g KClO3 contains 48 g O.
Hence, 100 g KClO3 contains
The percentages of K, Cl and O in KClO3 are 31.9%, 28.9% and 39.1%, respectively.
17. Urea is a very important nitrogenous fertilizer. Its formula is CON2H4.Caleulate the percentage of carbon in urea. (C=12, O=16, N=14 and H=1)
Solution
|
Element |
No. of atoms |
Atomic mass |
Total |
|
N |
2 |
14 |
28 |
|
C |
1 |
12 |
12 |
|
H |
4 |
1 |
4 |
|
O |
1 |
16 |
16 |
[12 + 16 + 28 + 4] = 60
Hence, relative molecular mass of urea = 60
Percentage of carbon = weight of carbon/Total weight of urea ×100
= 12/60 ×100
= 20%